Understanding Diabetes: is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It disrupts the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, leading to serious health consequences if left unmanaged. This article explores the causes, prevention strategies, and treatment options for diabetes in detail, providing a comprehensive understanding of the condition.
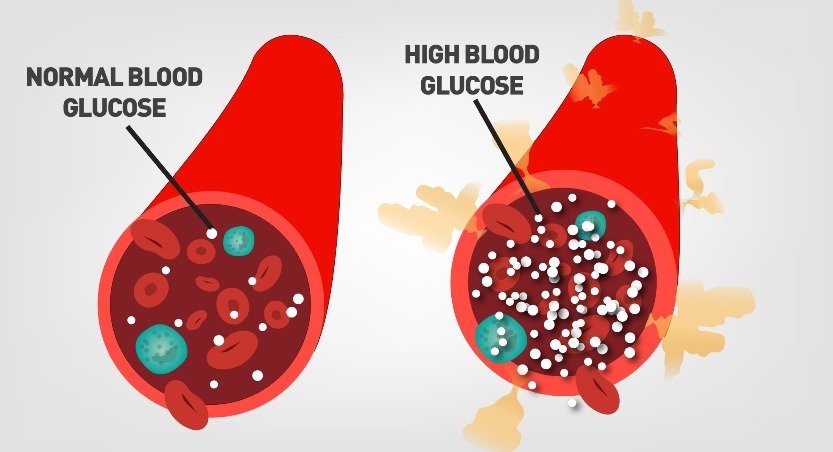
What is Diabetes?
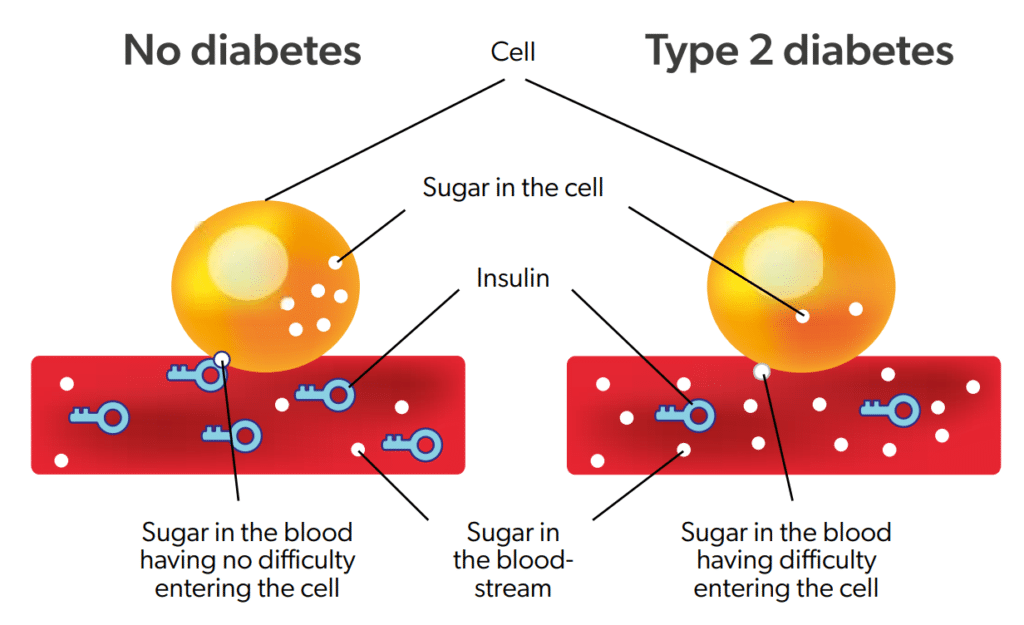
Diabetes occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the entry of glucose into cells, where it is used for energy. Without proper insulin function, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
Diabetes is classified into several types, the most common being Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Each type has distinct causes, risk factors, and management requirements.
Causes of Diabetes
The causes of diabetes vary depending on the type, but all types involve a disruption in the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar. Below are the specific causes and contributing factors for each type:
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This leads to a complete lack of insulin production. While the exact cause is unknown, several factors are believed to contribute:
- Genetics: A family history of Type 1 diabetes increases the risk.
- Environmental Factors: Viral infections, such as enteroviruses, may trigger the autoimmune response.
- Immune System Dysregulation: An overactive immune response mistakenly targets healthy pancreatic cells.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. Over time, the pancreas may also produce insufficient insulin. Factors contributing to Type 2 diabetes include:
- Lifestyle Factors: A sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy eating habits, and obesity are major contributors.
- Genetics: A strong family history of diabetes increases susceptibility.
- Age: Risk increases with age, particularly after 45.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and South Asians, have a higher risk.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that impair insulin action. Risk factors include:
- Obesity: Pre-pregnancy obesity increases the likelihood.
- Age: Women over 25 are at higher risk.
- Family History: A history of diabetes in close relatives.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A condition associated with insulin resistance.
Other Types of Diabetes
Other rare forms of diabetes can result from:
- Genetic Mutations: Monogenic diabetes, such as MODY (Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young).
- Medical Conditions: Pancreatic diseases, such as pancreatitis.
- Medications: Long-term use of steroids and some antipsychotic drugs.
Prevention Strategies
While Type 1 diabetes cannot currently be prevented, Type 2 and gestational diabetes can often be avoided or delayed through proactive measures. Here are the most effective strategies:
Understanding Diabetes:
1. Healthy Eating Habits
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in preventing diabetes. Key dietary practices include:
- Emphasize Whole Foods: Opt for whole grains, fresh vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds. These foods have a low glycemic index and help maintain steady blood sugar levels.
- Limit Sugars and Refined Carbs: Avoid sugary drinks, pastries, and processed foods that cause blood sugar spikes.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of unsaturated fats, such as olive oil, avocado, and fatty fish, while minimizing saturated and trans fats.
- Portion Control: Eating moderate portions prevents overeating and weight gain.
2. Regular Physical Activity
Understanding Diabetes: improves insulin sensitivity and helps maintain a healthy weight. Recommendations include:
- Aerobic Exercise: Engage in activities like brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week.
- Strength Training: Include resistance exercises like weight lifting or yoga twice a week to build muscle and improve metabolism.
- Daily Movement: Incorporate physical activity into your daily routine, such as taking the stairs or walking during breaks.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, increases insulin resistance. Losing even a small percentage of body weight—5% to 7%—can significantly lower the risk of Type 2 diabetes.
4. Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol
- Smoking: Tobacco use contributes to insulin resistance and inflammation.
- Alcohol: Excessive consumption can lead to weight gain and impair insulin function. Moderate drinking is advised—up to one drink per day for women and two for men.
5. Regular Medical Checkups
Routine health screenings can identify risk factors early. Tests include:
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS): Measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
- HbA1c Test: Reflects average blood sugar levels over the past three months.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Assesses how well the body handles glucose.

Treatment Options
Effective management of diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring. Treatment plans are tailored to the type of diabetes and individual needs.Understanding Diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Treatment for Type 1 diabetes focuses on insulin replacement and blood sugar management:
- Insulin Therapy: Delivered via injections or insulin pumps, it mimics natural insulin production.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Provides real-time blood sugar readings to guide insulin dosing.
- Healthy Diet: Focus on consistent carbohydrate intake to stabilize blood sugar.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps improve glucose utilization but requires careful planning to avoid hypoglycemia.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Management of Type 2 diabetes often involves a combination of lifestyle interventions and medications:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Diet, exercise, and weight loss remain foundational.
- Oral Medications: Common options include metformin (reduces glucose production in the liver), sulfonylureas (stimulate insulin release), and SGLT2 inhibitors (increase glucose excretion in urine).
- Injectable Medications: GLP-1 receptor agonists improve insulin sensitivity and promote weight loss.
- Insulin Therapy: Required in advanced cases when other treatments are insufficient.
3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes management focuses on protecting both mother and baby:
- Dietary Adjustments: A balanced diet tailored to manage blood sugar.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Frequent testing ensures levels stay within target ranges.
- Insulin Therapy: Safe for use during pregnancy if lifestyle changes are not enough.
4. Emerging Treatments
- Artificial Pancreas: Combines CGM and insulin pumps for automated blood sugar control.
- Islet Cell Transplants: Experimental procedures to restore insulin production.
- Medications for Weight Loss: New drugs targeting obesity are showing promise in diabetes prevention and management.
Understanding Diabetes:

Complications of Diabetes
When diabetes is poorly managed, it can lead to severe complications that affect multiple organ systems. Common complications include:
1. Cardiovascular Disease
- Increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and hypertension.
- Prevention: Control blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
2. Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
- Symptoms: Numbness, tingling, or pain in extremities.
- Prevention: Maintain stable blood sugar levels.
3. Kidney Damage (Nephropathy)
- Can lead to chronic kidney disease or kidney failure.
- Prevention: Monitor kidney function regularly and control blood pressure.
4. Eye Damage (Retinopathy)
- Can result in vision loss or blindness.
- Prevention: Annual eye exams and blood sugar control.
5. Foot Problems
- Poor circulation and nerve damage increase the risk of ulcers and infections.
- Prevention: Regular foot care and prompt treatment of wounds.
6. Skin and Dental Issues
- Increased risk of infections, slow wound healing, and gum disease.
- Prevention: Practice good hygiene and attend regular checkups.
Living Well with Diabetes
While diabetes is a lifelong condition, effective management allows individuals to lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Key strategies include:
- Education: Understanding the condition empowers better decision-making.
- Support Systems: Join support groups or connect with healthcare providers.
- Technology: Use apps and devices for tracking blood sugar, diet, and exercise.
- Mental Health Care: Address the emotional impact of living with diabetes.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex but manageable condition. Understanding its causes, taking proactive steps for prevention, and adhering to individualized treatment plans can significantly reduce its impact. With ongoing research and advancements in medical care, the outlook for people living with diabetes continues to improve.
Sources of some information
Sources of some information
Click here to learn more about this topic in a related article.
Click here to learn more about this topic in a related article.



[…] Diabetes and sexual dysfunction are closely related due to the physiological, hormonal, and psychological effects of the disease. Below is an overview of this relationship for both men and women: […]
[…] Click here to learn more about this topic in a related article. […]
[…] Click here to learn more about this topic in a related article. […]
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
What can I help you with?