Effective money management is a cornerstone of financial well-being. Whether you’re managing personal finances or overseeing a household budget, understanding how to handle your money can make the difference between financial security and chronic stress. This article explores the key principles, strategies, and tools that empower individuals to take control of their finances, build wealth, and achieve their goals.
Understanding the Basics of Money Management
What Is Money Management?
Money management refers to the process of budgeting, saving, investing, spending, and overseeing financial resources. It involves creating a plan to allocate your income efficiently to meet both current needs and future goals.
Why Is Money Management Important?
- Financial Security: Proper money management ensures you have enough resources to cover emergencies and unforeseen expenses.
- Stress Reduction: Knowing your finances are under control can significantly reduce stress and improve mental health.
- Goal Achievement: Effective planning helps you save for major milestones, such as buying a home, starting a business, or retiring comfortably.
- Debt Avoidance: Managing money wisely helps prevent excessive debt, which can hinder financial progress.

Key Principles of Money Management
1. Spend Less Than You Earn
The foundation of financial success lies in living within your means. Avoid overspending by differentiating between needs and wants, and allocate your income wisely.
2. Create a Budget
Budgeting involves tracking your income and expenses to understand where your money goes. Use the 50/30/20 rule as a guideline:
- 50%: Necessities like rent, groceries, and utilities.
- 30%: Discretionary spending, such as entertainment or dining out.
- 20%: Savings and debt repayment.
3. Build an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund acts as a financial safety net. Aim to save 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses in an easily accessible account.
4. Pay Yourself First
Treat savings as a non-negotiable expense. Automate transfers to a savings or investment account to ensure consistent contributions.
5. Avoid High-Interest Debt
High-interest debt, such as credit card balances, can erode wealth over time. Prioritize paying off such debt to free up resources for other financial goals.
6. Invest Wisely
Investing allows your money to grow over time. Diversify your portfolio to manage risk and focus on long-term objectives.
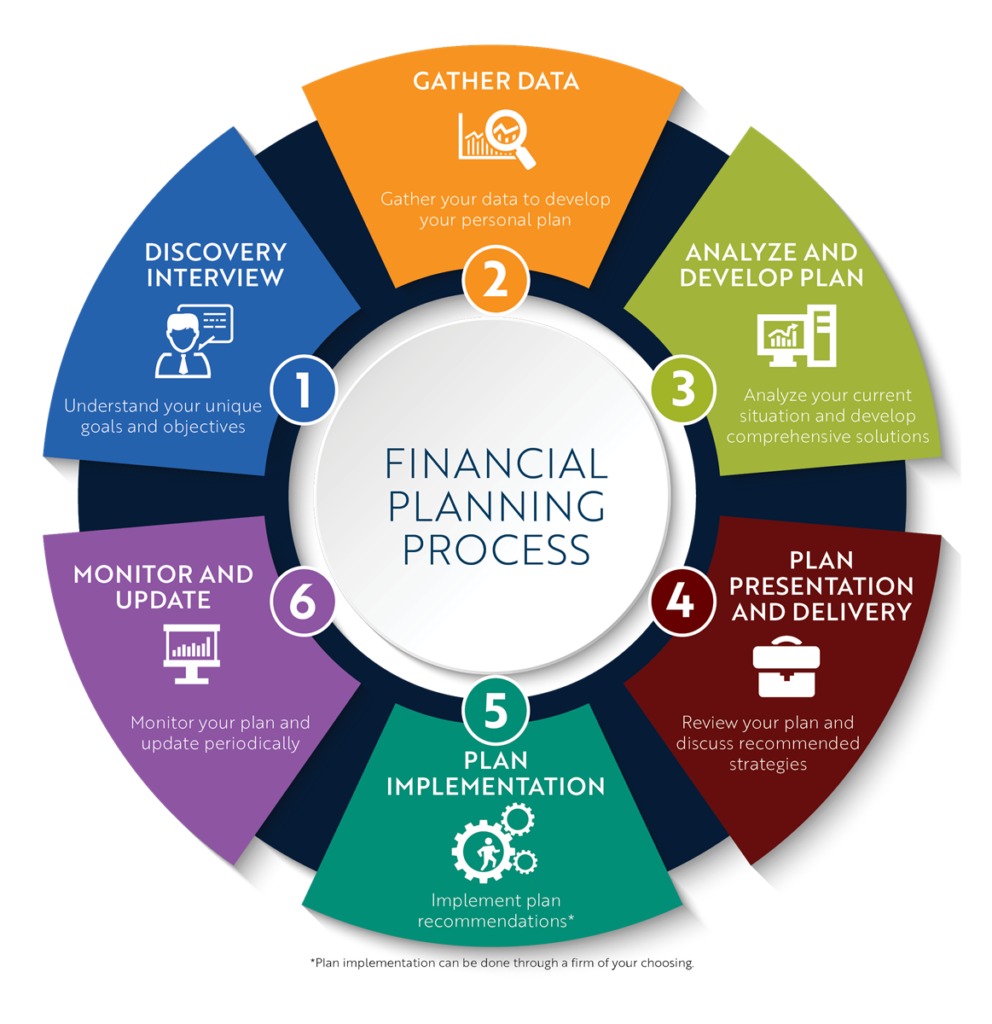
Practical Steps for Effective Money Management
Step 1: Assess Your Financial Situation
Start by evaluating your current financial health. Consider the following:
- Net Worth: Subtract liabilities from assets to determine your overall financial standing.
- Cash Flow: Track monthly income and expenses to identify spending patterns.
- Debt Levels: List all debts, including interest rates and minimum payments.
Step 2: Set Financial Goals
Define short-term, medium-term, and long-term goals. Examples include:
- Short-term: Saving for a vacation.
- Medium-term: Paying off student loans.
- Long-term: Building a retirement fund.
Step 3: Create a Personalized Budget
Use a budgeting tool or app to allocate your income effectively. Categories may include:
- Housing
- Transportation
- Savings
- Debt repayment
- Entertainment
Step 4: Implement Savings Strategies
- Automate Savings: Set up automatic transfers to a savings account.
- Cut Expenses: Identify areas to reduce spending, such as dining out or subscription services.
- Increase Income: Consider side hustles or freelance work to boost earnings.
Step 5: Manage Debt Strategically
Adopt one of these methods to eliminate debt:
- Debt Snowball: Pay off smaller debts first to build momentum.
- Debt Avalanche: Focus on debts with the highest interest rates to save money over time.
Step 6: Start Investing
Begin with low-risk investments, such as index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Over time, diversify your portfolio with stocks, bonds, and real estate.

Tools and Resources for Money Management
- Budgeting Apps
- Mint
- YNAB (You Need A Budget)
- PocketGuard
- Financial Planning Tools
- Personal Capital
- Quicken
- Goodbudget
- Educational Resources
- Books: The Total Money Makeover by Dave Ramsey, Rich Dad Poor Dad by Robert Kiyosaki
- Podcasts: The Financial Independence Podcast, How to Money
- Online Calculators
- Retirement calculators
- Loan repayment calculators
- Savings growth calculators
Overcoming Common Money Management Challenges
Challenge 1: Impulse Spending
Solution: Use a 24-hour rule for non-essential purchases. If you still want the item after 24 hours, consider buying it.
Challenge 2: Lack of Discipline
Solution: Automate financial tasks, such as bill payments and savings contributions.
Challenge 3: Unexpected Expenses
Solution: Maintain an emergency fund and consider insurance for major risks.
Challenge 4: Insufficient Income
Solution: Explore new job opportunities, request a raise, or pursue additional qualifications to increase earning potential.
The Psychological Aspect of Money Management
Understanding Money Mindsets
Your attitude towards money plays a significant role in financial decisions. Common money mindsets include:
- Scarcity Mindset: Viewing money as limited and focusing on saving.
- Abundance Mindset: Believing in the potential for wealth creation and taking calculated risks.
Cultivating Healthy Financial Habits
- Practice Gratitude: Focus on what you have rather than what you lack.
- Set Realistic Expectations: Avoid comparing yourself to others and focus on your financial journey.
- Celebrate Milestones: Reward yourself for achieving financial goals to stay motivated.

Advanced Money Management Strategies
Leverage Tax Advantages
- Retirement Accounts: Contribute to tax-advantaged accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs.
- Tax Deductions: Maximize deductions for education, medical expenses, or charitable donations.
Optimize Credit Use
- Maintain a high credit score by paying bills on time and keeping credit utilization low.
- Use rewards credit cards strategically for cashback or travel benefits.
Pursue Passive Income Streams
- Real Estate: Invest in rental properties or Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs).
- Dividend Stocks: Earn regular income from dividends.
- Digital Products: Create and sell eBooks, online courses, or apps.
Estate Planning
Prepare for the future by creating a will, designating beneficiaries, and considering trusts for wealth transfer.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Money Management
Case Study 1: Overcoming Debt
John, a 35-year-old teacher, used the debt snowball method to pay off $20,000 in credit card debt within three years. By cutting unnecessary expenses and taking on a part-time tutoring job, he achieved financial freedom.
Case Study 2: Building Wealth
Maria, a 40-year-old entrepreneur, started investing 20% of her income in index funds. Over 15 years, her portfolio grew significantly, enabling her to semi-retire and focus on passion projects.
The Role of Financial Advisors
If managing finances feels overwhelming, consider consulting a financial advisor. They can help with:
- Retirement planning
- Investment strategies
- Tax optimization
- Estate planning
Conclusion
Mastering money management is a journey that requires discipline, knowledge, and consistency. By adopting sound financial principles, leveraging tools and resources, and maintaining a growth mindset, you can take charge of your financial future. Whether your goal is to pay off debt, save for a major purchase, or retire early, the strategies outlined in this guide can set you on the path to success.
Remember, the key to financial freedom lies in taking small, consistent steps every day. Start today and watch your financial confidence and stability grow.
Would you like to adjust the tone, include more case studies, or focus on specific aspects like investing or debt management? Let me know!




[…] Click here to learn more about this topic in a related article. […]
[…] Click here to learn more about this topic in a related article. […]