Between Diabetes and Sexual Dysfunction:, a chronic metabolic condition characterized by high blood glucose levels, is a well-documented risk factor for sexual dysfunction. Affecting millions of individuals worldwide, diabetes poses challenges not only to physical health but also to emotional well-being and intimate relationships. This article explores the intricate relationship between diabetes and sexual dysfunction, its causes, impact on individuals, and strategies for management and treatment.

Understanding the Link Between Diabetes and Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction encompasses various issues, including reduced libido, difficulty achieving or maintaining erections in men, and challenges with arousal or discomfort during intercourse in women. The interplay between diabetes and sexual health arises from a combination of physiological, hormonal, and psychological factors.
1. Physiological Factors
- Vascular Damage: Diabetes is associated with damage to blood vessels, known as diabetic angiopathy. This can impair blood flow to genital areas, a critical factor for achieving and maintaining an erection in men and arousal in women.
- Neuropathy: Persistent high blood sugar levels can damage nerves (diabetic neuropathy), disrupting the transmission of signals needed for sexual response.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Diabetes can lower testosterone levels in men, leading to reduced libido. In women, it may disrupt estrogen levels, affecting lubrication and arousal.
2. Psychological Factors
- Stress and Anxiety: Managing a chronic condition like diabetes can lead to psychological stress, impacting sexual desire and performance.
- Depression: People with diabetes are more prone to depression, which can diminish interest in sexual activity and affect overall intimacy.
- Body Image Concerns: Weight changes or diabetes-related complications may affect self-esteem, contributing to reduced sexual confidence.
3. Medication Side Effects
Some medications for diabetes and related conditions, such as hypertension, may have side effects that contribute to sexual dysfunction.
How Diabetes Affects Sexual Function in Men
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED):
- ED is highly prevalent among men with diabetes, affecting up to 75% of those with the condition.
- The dual impact of vascular damage and neuropathy often makes achieving and sustaining erections challenging.
- Retrograde Ejaculation:
- Nerve damage from diabetes can lead to a condition where semen flows backward into the bladder instead of exiting through the penis during ejaculation.
- Reduced Libido:
- Hormonal changes, coupled with psychological stress, may result in diminished sexual desire.
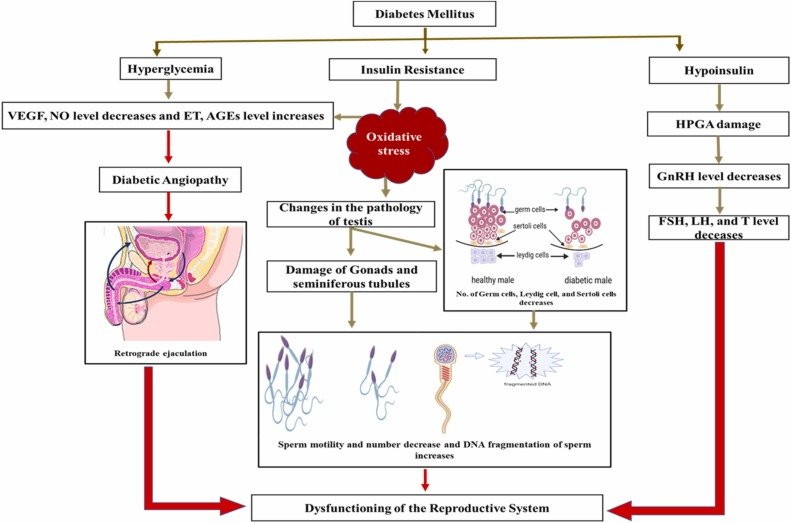
How Diabetes Affects Sexual Function in Women
- Vaginal Dryness:
- High blood glucose levels may affect the production of natural vaginal lubrication, causing discomfort during intercourse.
- Decreased Arousal and Orgasm:
- Neuropathy and impaired blood flow can reduce sensitivity in genital tissues, making arousal and orgasm difficult.
- Increased Risk of Infections:
- Women with diabetes are more prone to yeast infections and urinary tract infections, which can disrupt sexual activity.
Management and Treatment Strategies
1. Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels is fundamental to preventing or mitigating sexual dysfunction. Improved glycemic control can reduce the risk of vascular and nerve damage.
2. Lifestyle Changes
- Regular Exercise: Enhances cardiovascular health and reduces stress, benefiting sexual health.
- Healthy Diet: Supports overall well-being and aids in weight management, improving self-esteem and energy levels.
- Avoiding Tobacco and Alcohol: Reducing these habits can improve circulation and nerve function.
3. Medical Treatments
- Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors (PDE5i): Medications like sildenafil (Viagra) are commonly prescribed for ED.
- Hormone Therapy: Testosterone replacement for men and estrogen creams or lubricants for women may address hormonal imbalances.
- Vacuum Devices: For men, vacuum erection devices can assist in achieving erections.
- Surgical Options: Penile implants may be considered in severe cases of ED.
4. Psychological Support
Counseling or therapy can address the psychological impact of diabetes and sexual dysfunction. Couple’s therapy may help partners navigate these challenges together.
5. Open Communication
Encouraging open dialogue with healthcare providers and partners is crucial. Many individuals feel hesitant to discuss sexual health, but addressing these concerns can lead to effective solutions.
Impact on Relationships and Quality of Life
Sexual dysfunction can strain relationships, leading to feelings of inadequacy, frustration, and reduced intimacy. Addressing these issues proactively is essential for preserving emotional connections and enhancing quality of life.

Conclusion
The relationship between diabetes and sexual dysfunction is both complex and multifaceted, intertwining physical, hormonal, and emotional dimensions that collectively impact an individual’s quality of life. Sexual dysfunction is often an overlooked consequence of diabetes, yet it significantly influences personal well-being and intimate relationships. Understanding the causes and effects of this connection is essential in empowering individuals to address these challenges with confidence and clarity.
For men, erectile dysfunction remains one of the most prevalent concerns, stemming from the interplay of vascular complications, nerve damage, and hormonal imbalances. Meanwhile, women face challenges such as vaginal dryness, decreased arousal, and an increased risk of infections, which not only affect their sexual health but also their emotional connection with partners. Beyond the physical, the psychological burden of diabetes—including anxiety, depression, and body image concerns—can exacerbate sexual dysfunction for both genders. Recognizing these interconnected factors provides the first step toward holistic management.
Effective management strategies begin with maintaining optimal blood sugar levels. Glycemic control plays a pivotal role in mitigating the risk of vascular and nerve damage, laying a foundation for improved sexual health. Coupled with this, lifestyle modifications—such as regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption—enhance cardiovascular health, boost energy, and elevate mood. These changes not only improve physical health but also foster a sense of self-confidence and well-being.
Medical interventions are invaluable for addressing persistent symptoms. Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil) have revolutionized the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men, offering a reliable solution for many. Similarly, hormone therapy—including testosterone replacement for men and estrogen creams or lubricants for women—can rectify imbalances that disrupt libido and arousal. In more severe cases, options such as vacuum devices, intracavernosal injections, or penile implants may be explored under the guidance of healthcare professionals. These treatments underline the importance of personalized medical care tailored to each individual’s needs.
Beyond physiological remedies, psychological support is critical. Therapy and counseling provide a safe space for individuals and couples to explore the emotional aspects of sexual dysfunction. By addressing underlying stressors, fostering open communication, and promoting mutual understanding, therapy can help rebuild intimacy and strengthen relationships. In this context, open dialogue with healthcare providers and partners becomes paramount. Discussing sexual health openly—despite societal taboos or personal discomfort—paves the way for effective solutions and improved relationships.
It is also crucial to acknowledge the broader impact on relationships and quality of life. Sexual dysfunction can erode intimacy, leading to feelings of inadequacy or frustration for both individuals and their partners. However, with proactive approaches and a supportive environment, these challenges can be addressed effectively. Rebuilding intimacy involves not only medical or therapeutic interventions but also nurturing empathy, patience, and understanding within relationships.
In conclusion, the challenges posed by diabetes-related sexual dysfunction are surmountable through a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, psychological support, and open communication. Empowering individuals with knowledge and encouraging proactive steps can transform their journey, fostering improved sexual health and strengthened emotional connections. By addressing these challenges holistically, individuals with diabetes can not only reclaim their sexual well-being but also enhance their overall quality of life and relational harmony.
For further information and resources, individuals are encouraged to consult reputable organizations such as the American Diabetes Association, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), and the Mayo Clinic. These platforms offer invaluable insights into managing diabetes and its associated complications, empowering individuals to lead fulfilling and healthy lives.
Further Reading
- American Diabetes Association – Sexual Health and Diabetes
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- Mayo Clinic – Diabetes and Sexual Health
By addressing the multifaceted challenges of diabetes and sexual dysfunction with knowledge and empathy, individuals and healthcare providers can pave the way for improved sexual health and intimate relationships.
Click here to learn more about this topic in a related article.
Click here to learn more about this topic in a related article.



[…] Click here to learn more about this topic in a related article. […]